Symptoms of worms in humans cannot always be noticed in time. Worm infestation often presents with symptoms similar to other illnesses, such as allergies or indigestion. Helminths parasitize in different parts of the human body. An infected person may experience liver failure, chronic colds or dermatoses without knowing the true cause of the health problems.
What are helminths
Worms in humans are parasitic worms that can vary in size. They can enter the human body through the mouth, nasal passages, eyes, urethra or anus. Most often, parasites live in the intestine, attached to its walls using suction cups, tentacles or peculiar teeth. Parasites can live in the tissues of the lungs and brain, on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, in muscles, in the liver and gallbladder.
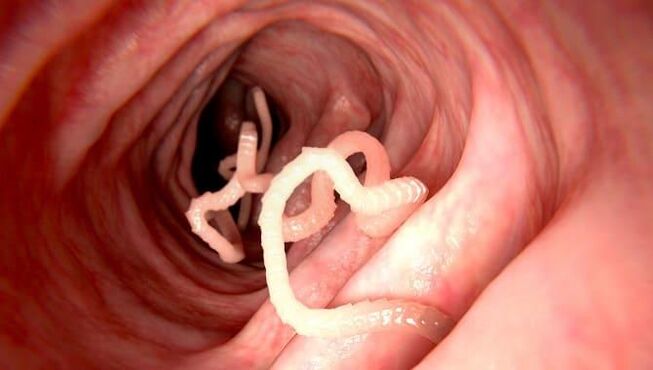
Worms feed on substances that enter the blood from the intestines, red blood cells and tissue juices.
Classification of helminthiasis: types of worms in humans
Different types of helminths can parasitize the human body. Medical helminthology divides them into groups taking into account the specificity of body shape:
- Round (nematodes)- have a holistic form in the form of a lemon, thread, barrel or spindle. The head and tail of nematodes are slightly pointed. The oral apparatus is characterized by three layers. Parasites move freely in soil, freshwater and the sea. The human body contains pinworms (which cause enterobiasis), roundworms, hookworms and trichinella, which are considered intestinal parasites. Guinea worms - these roundworms spread through the subcutaneous tissue.
- Ribbon (cestodes). These include the following types of parasites: cattle, swine, dwarf tapeworm, broad tapeworm. Its body resembles a finely segmented ribbon, the length of which can reach 10 meters or more. The front part of parasitic worms is equipped with suction cups and hooks with which they are attached to the intestinal walls. Echinococci have a complex attachment system - 4 suction cups surrounded by two rows of hooks.
- Trematodes (worms)— this type of worm is characterized by specific habitats in the body: the gallbladder, the bile ducts. Representatives of the worm class are Siberian worms (4-13 mm), fasciola (length 3-7 cm).
The vital activity of helminths interferes with the normal functioning of the human body. The parasites poison the blood with toxins, causing the person to feel dizzy, itchy skin, coughing and poor sleep at night.
How do you get infected with helminths?
Everyone should know why worms appear in humans and where they live in the body:
- Nematodes and dwarf flat tapeworm enter the body through dirty hands, eating unwashed vegetables and drinking dirty water. Habitat: intestines.
- Trichinella, beef and pork tapeworm - infection occurs when eating poorly thermally processed meat (beef, pork). Location: intestine.
- Opisthorchis, broad tapeworm (class of trematodes or tapeworms). A person can become infected by eating raw, under-salted or under-cooked fish. In fish, the parasite larvae live in the fat layer and muscles. In humans, they settle in the liver and gallbladder.
- Echinococci, Siberian fluke, and fluke are transmitted through contact with an infected dog; Less commonly, cats are the source of infection. Helminths can parasitize the human liver, lungs, kidneys and heart. They develop inside echinococcal cysts.
What do worms look like in human feces?
A person may see dead roundworms in stool 3-4 days after taking anthelmintic tablets. The length of these parasites living in the human body can reach 40 cm, their edges are pointed and their body is white.
Pinworms usually leave the body alive a few hours after consuming milk with garlic, very salty or spicy foods. Small white worms (up to 12 mm long) with sharp edges are clearly visible in the feces and around the anus.
Large flatworms or tapeworms are almost impossible to see entirely (length 3 to 10 m). After baiting, the worms exit the body in rotting fragments.
Signs of the presence of worms in humans
In helminthic infestation, symptoms in adults and children often resemble the manifestations of other diseases. This is due to the location (respiratory tract, liver, gallbladder) and the life process of the worms.
During the acute period
The acute phase is believed to be asymptomatic. But in most cases, the first signs of worms are mild and the person ignores the parasitic disease. Less commonly, in an infected person, signs of helminthiasis in the body occur with fever, nausea and vomiting. The person feels weak and loses their appetite.
In the chronic phase
Symptoms of chronic helminthiasis depend on the type of worms, their number and habitat.
Intestinal helminthiasis
Symptoms of worms in an adult in the intestine:
- deterioration of digestion;
- intense pain in the navel area;
- intestinal dysfunction;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss;
- pale skin;
- bruises under the eyes;
- anal itching.

Against the background of gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal obstruction may occur. The pathological condition is manifested by paroxysmal pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting with the presence of fecal odor.
Extraintestinal helminthiasis
The main signs of helminth infection in the liver, gallstones and lungs:
- constant fatigue;
- nervous breakdown;
- paroxysmal pain in the epigastric region;
- decreased performance;
- greasy, foul-smelling stools (steatorrhea);
- hives, itchy skin;
- chest pain;
- chronic dry cough;
- change in skin color.
Extraintestinal parasites (giardia, opistorchis, fasciola) can cause not only headaches or skin diseases, but also depression. Typically, a pathological condition occurs if the symptoms of a skin allergy do not disappear for a long time (itching, dry skin, rash) or reappear after treatment.
How to detect worms: diagnosis of helminthic infestations
To diagnose helminths, feces are collected from the worm eggs. But the analysis does not always show a positive result in the presence of parasites. Firstly, not all types of worms are determined in this way. Secondly, the time of presentation of feces for analysis may not coincide with the time of parasite reproduction. A repeat test for worm eggs is done after 2-3 days. If the result in the presence of symptoms is negative, the following examination methods may be prescribed:
- Blood analysis- an elevated level of eosinophilic leukocytes and low hemoglobin levels indicate worm infection.
- Duodenal probing- helps identify opisthorchiasis, giardiasis and other extraintestinal worms in humans by examining secretions from the duodenum.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and other parts of the human body— the gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder, its ducts, pancreas, muscles, brain, lungs are examined for the presence of pathological changes characteristic of the life of worms (seals, cysts, nodules, blockages).
- chest X-ray- carried out if pulmonary parasites are suspected (roundworms, echinococci, tapeworm larvae are detected).
- Computed tomography- to detect worms in the human brain, eyes and lungs.
- Capsule endoscopy- to identify ribbon parasites.
- ELISA— detects antibodies in the blood to most known parasites.
To assess the severity of damage caused to the body by worms, an immunological study is prescribed. Helps identify weaknesses in the human immune system. After that, complex therapy for the pathological condition is prescribed.
How to get rid of worms quickly and effectively
It is best to learn how to remove helminths from the human body at a consultation with a parasitologist. Treating worms without medical advice can cause poisoning and liver dysfunction.
Diet and hygiene features
Treatment of helminthiasis in adults and children must be accompanied by a diet that helps to quickly remove worms and cleanse the body of toxins. It is necessary to exclude from the menu products that contribute to the vital activity of parasites or intoxication of the body:
- meat, lard;
- all kinds of sweets;
- fresh milk;
- baked goods;
- wheat porridge, pasta;
- coffee, alcohol.

The daily diet should include a fresh carrot salad, fermented milk products with probiotics, eggs, freshly prepared vegetable juices, potato, vegetable and mushroom dishes. The duration of the diet during worm treatment is determined by the doctor.
Hygiene procedures for helminthic infestation include frequent and thorough hand washing with soap. The procedure must be carried out before meals, after going to the bathroom and upon returning from the street. Bed linen is changed 2 to 3 times during the week. Be sure to iron after washing. After bathing, always take a clean towel with you.
Medicines
Treatment of worms in adults and children is carried out with the following medications:
- Broad-spectrum anthelmintic drug of the benzimidazole type - effective against nematode worms and trematodes. Contraindicated in children under 2 years of age, prescribed with caution to pregnant and lactating women. The dosage and frequency of use of the medicine depend on the type of worms. For roundworms and mixed infestations, 1 tablet is prescribed. 2 times a day for three days. Enterobiasis is treated for three days in a row, taking 1 tablet per day. The course is repeated after 21 days. Echinococci in an adult are eliminated by increasing the dosage of the drug: the first 3 days - 500 mg in the morning and evening, the next three days - 500 mg three times a day until complete recovery from the parasites. The duration of treatment for echinococcosis is determined by the doctor (from 4 to 6 weeks).
- Broad-spectrum anthelmintic drug from the pyrazinisoquinoline group. Contraindicated for children under 4 years of age and pregnant women (1st trimester). Effective for muscle/tissue worms. Urogenital (the worms live in the blood vessels close to the bladder), intestinal and abdominal schistosomiasis are treated with a single dose of the medication (40 mg/10 kg). In severe forms of parasitic vascular pathology, tablets are taken 3 times a day (every 6 hours) at a dose of 20-25 mg/10 kg.
- Broad-spectrum drug from the benzimidazole group. Not prescribed for children under 2 years of age, pregnant or lactating women. Adults receive 400 mg/day once and children at a rate of 60 mg/10 kg for intestinal helminthiasis. For parasites in the brain, adults are given 800 mg/day, children - 15 mg/kg, the course of treatment is 8-30 days.
Anthelmintic medications are toxic. They are not prescribed for people with liver failure, ulcerative colitis, or Crohn's disease.
Traditional methods
How to cure worms with home remedies:
- Grind the flaxseed (1 tablespoon). Pour the powder into 0. 5 liters of cold water. Bring the mixture to a boil, cook over low heat, covered, for 20 minutes. Drink 100 ml morning and evening on an empty stomach for 10 days in a row. The recipe helps against almost all parasites that can live in the human body - pinworms, tapeworms, Giardia.
- Grind 300 g of dried, but not fried, pumpkin seeds. Add enough hot boiled water to the powder to make a paste. Add a large spoonful of honey. Eat the entire mixture on an empty stomach. After 4 hours, take a laxative. The recipe is effective for intestinal worms in humans.

Pumpkin seeds are an allergenic product, so itching of the skin may occur during worm treatment. An anti-allergy pill will help to deal with this.
Which parasites can only be removed surgically?
Surgical treatment of helminthiasis requires the following conditions:
- Obstruction of the intestinal tract - a pathological condition is provoked by roundworms, tapeworms, pinworms and other worms.
- Perforation of the intestinal wall - the bovine tapeworm makes a hole and exits into the human abdominal cavity.
- Parasitic cholecystitis with subsequent necrosis of the pancreas is the blockage of the bile duct by a ribbon parasite.
Most often, surgery is used for echinococcosis. Parasitic cysts in an infected person in the lungs, kidneys, liver and spleen are removed by laparotomy or laparoscopy.
How dangerous is helminth infestation for the body?
If left untreated, the pathology takes on a chronic form. The most dangerous thing that can happen to the body during a severe form of the disease is the destruction of tissues of internal organs, suffocation and the appearance of blindness.
How to protect yourself from infections
Prevention of helminthic infestation in the body requires a person to:
- Carefully observe the rules of personal hygiene.
- Treat parasites in pets immediately.
- Heat treat the fish for 60 minutes, and the meat for 2-3 hours.
In people with strong immunity, worm eggs are neutralized, so the immune system must be constantly strengthened. To do this, it is enough to lead a healthy lifestyle and periodically take vitamin and mineral complexes.