When it comes to parasites in the body, most people think of worms in the intestines. However, other parasites are also common, which are quite difficult to diagnose and affect organs other than the intestines.
These are the simplest microscopic (most often parasites), which may not appear at all for a long time. However, the simplest parasites can cause significant damage to the body.
Giardia
Giardia is a microscopic flagellate parasite that has two nuclei and two sets of organelles.
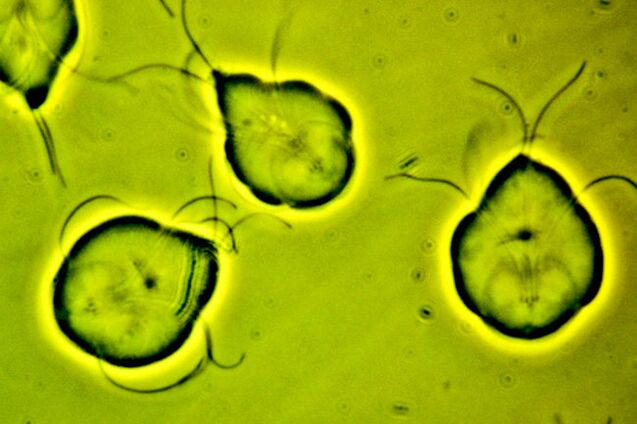
Giardiasis in humans is caused by the most common type of parasite - intestinal lamblia. In addition to humans, other mammals and birds can also be infected with them. The parasite can form a cyst in the localization organ.
Giardia is present in poorly treated tap water, as well as in natural sources - springs, wells. They can be found in the meat of an infected animal or poultry, in small amounts in the feces of an infected animal, sometimes survive in the soil as they are present in wild vegetables and fruits.
Usually, the infection occurs via the fecal-oral route, that is, for the invasion to develop, it is necessary to swallow a significant number of cysts of the parasite. Usually, children from three months and adults get sick.
Most of the time, the disease is asymptomatic and the patient learns by chance. But sometimes there is some symptomatology (constantly or intermittently). Symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract are revealed:
- Stomachache;
- Swelling;
- Nausea, sometimes vomiting;
- Rumbling in the stomach;
- Constipation and diarrhea alternate;
- Biliary tract dyskinesia;
- Skin allergies;
- General weakness.
As an intracellular parasite, lamblia is mainly treated with metronidazole. However, in the first phase of therapy, it is necessary to remove the intoxication and normalize the functioning of the bile ducts. Only after that is antiparasitic therapy prescribed. Then, therapy is performed with the aim of restoring the body's defenses and increasing immunity.
Amoeba
Amoebas are the simplest human parasites that cause amoebic dysentery or amoebiasis.
There are also varieties of amoeba that can affect the eyes. It causes amoebic encephalitis but is less common. The invasion is not the most common, only 10% of people are sick, according to the WHO (while for giardiasis, this number, according to some sources, is 50%).
Amoebas are transmitted exclusively through the fecal-oral route, that is, as in the previous case, the amoebas form cysts that must be swallowed for the infection to develop.
The probability of infection is greater in countries with hot climates and poor sanitary conditions. Cysts can retain the ability to infect for a long time while in soil, water, vegetables and fruits grown in contaminated soil. Cockroaches and flies carry these cysts to some extent.
Like intracellular parasites, amoebas cause symptoms only 7 to 10 days after infection. Symptoms of colitis appear: abdominal pain (in the lower part), general weakness, a slight increase in body temperature. Most of the time, the liver is affected, because after two to three weeks pains appear, the organ grows and thickens.
Toxoplasma
Toxoplasmosis is a disease causing Toxoplasma gondi. It is the simplest organism, which is distributed mainly by representatives of the feline family who are its carriers. An infected person is also capable of spreading.
It is transmitted via the fecal-oral route. You can become infected by eating poorly processed meat from infected animals and birds, as well as eggs. To a lesser degree, but still capable of being transmitted by blood, in the presence of wounds (eg when working with contaminated soil in the garden) as well as in contact with mucous membranes.
It is usually asymptomatic and is diagnosed by chance, like many viruses, for example, during an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In the acute form, healing usually occurs independently. Pregnant women require treatment with pyrimethamine drugs (which are used to treat intracellular parasites).
Plasmodium
Plasmodia are intracellular parasites that cause malaria. Five types of pathogens are capable of parasitizing in humans. Furthermore, they are located in the blood, being in the membranes of your cells.
The disease is transmitted through the blood (for example, through a transfusion). It is also tolerated by some types of mosquitoes when bitten, as the intermediate hosts of Plasmodium are mosquitoes. As a result, the person becomes infected with malaria.
These mosquitoes (and hence the disease) are common in hot countries, particularly Africa.
Malaria has severe symptoms that begin 5 to 7 days after infection. The first symptoms are joint pain, fever, severe chills. Then headache, enlarged spleen junction.
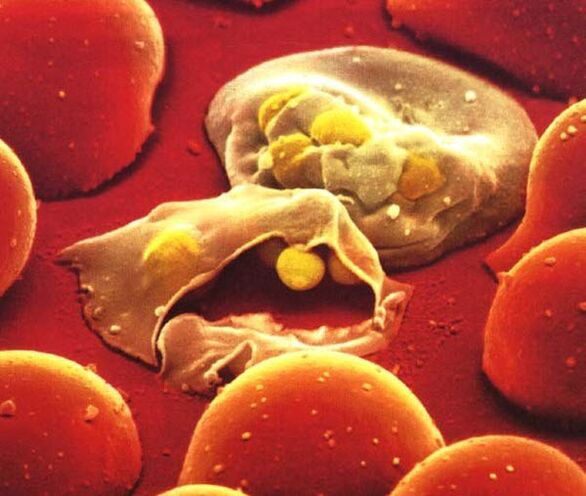
Treatment is carried out with quinine preparations strictly under the supervision of a doctor.
Trichomonas
These are the simplest human parasites that cause trichomoniasis. It affects the human genitourinary system. It is the most common sexually transmitted disease and also the most common disease of the genitourinary system.
Transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. In women, they live in the vagina, Trichomonas in men - in the urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate.
In women, symptoms are as follows: vaginal discharge, itching and redness of the skin on the genitals, pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse, inflammation of the vaginal mucosa. In men: urethral discharge (rarely, with blood), pain when urinating, symptoms of prostatitis with prostate damage.
It is necessary to treat the disease in both partners. It is treated with anti-trichomonasal drugs strictly individually and under the supervision of a physician. In some cases, immunological or symptomatic therapy is required.