Human parasites can inhabit all organ systems. The vital activity of helminths can become a prerequisite for the development of cancer, and microscopic fungi and mites can cause allergies.
The human body can be inhabited by at least 300 species of parasites, including representatives of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, microscopic fungi, helminths (parasitic worms), individual arthropods. These organisms not only consume the nutrients assimilated by the host, but also poison it with the products of its vital activity. According to the canons of modern medicine, the concept of "parasite" does not apply to pre-nuclear (prokaryotic) organisms: bacteria and viruses. It features protozoa, fungi, worms, arthropods that live in the host's body, subsisting exclusively on it.
Microparasites
Human and animal organisms are a fertile environment for the life of microscopic fungi as well as protozoa. Indiscernible to the naked eye, they cause damage to the skin and internal organs.
Protozoan parasites
An infection caused by a protozoan is called a protozoan. These diseases are common in tropical areas and also in temperate latitudes. About 50 species of protozoa parasitize human organs and tissues. They can be infected through sexual contact, food or insect bites.
Giardiasis is very common. Up to 40% of children and 10% of adults have this pathology. Lamblia's favorite habitat is the small intestine. The disease can be accompanied by digestive disorders, allergic reactions, although it is often asymptomatic. The pathogen is transmitted through food - with unboiled water and contaminated food.
According to various sources, 30 to 50% of the world's population is infected with toxoplasmosis. Its pathogen often lives in the host's organism without any clinical manifestations. Toxoplasma represents the greatest danger for pregnant women: it causes intrauterine fetal death or severe malformations. Infection occurs through contact with domestic mammals (cats, rabbits, rodents) and by eating raw meat.
The most common sexually transmitted infection is the protozoan. This is trichomoniasis. More than 150 million people are infected worldwide every year. The manifestations of the disease are determined by which organs are affected. In women, Trichomonas lives in the vagina, causing inflammation, accompanied by urethritis. In men, the protozoan affects the prostate, the seminal vesicles, in severe cases leading to prostatitis, although more often the infection is asymptomatic.
In tropical regions, diseases such as malaria, leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness are widely known. Its causative agents are plasmodia, leishmania and trypanosomes, respectively. The parasites are transported by blood-sucking insects: mosquitoes, tsetse flies, triatomaceous insects. By biting animals or sick people, they acquire and distribute the agents that cause these diseases.
Parasitic fungi
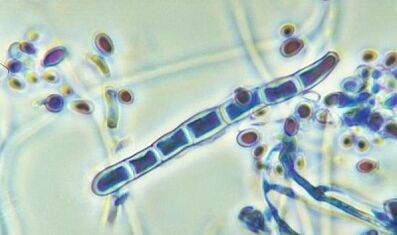
About 100 species of fungi are known to be quite dangerous to humans. Its ideal habitat is the hot and humid areas of the body, for example, the interdigital spaces. However, these organisms can also infect the skin and other areas of the human body.
Fungi of the species Trichophyton, Microsporum, Epidermophyton cause dermatomycosis: ringworm and pityriasis versicolor, lesions on the feet, scalp, rarely mucous membranes. The agents that cause these diseases can be transmitted to humans by animals or sick people. In severe cases, bacterial infections join dermatomycosis.
Mold fungi and their spores are no less harmful to humans. They cause diseases like this:
- penicellosis; mucose;
- aspergillosis.
These pathologies are characterized by inflammation of all parts of the respiratory tract, without exception, otitis media and various allergic reactions. In severe cases, parasitic fungi cause pneumonia and also bronchial asthma. People with weakened immunity and chronic illnesses are more susceptible to yeast infections.
Helminths
The favorite habitat of parasitic worms is the digestive tract of humans and animals, in which they feed on the digested food, bile and blood of the host. All helminths belong to the following classes:
- roundworms (nematodes);
- flatworms (worms and worms).
Flat parasitic worms
Eggs and larvae of trematodes (flatworms) usually enter the human body with raw water, unwashed vegetables, meat and fish not sufficiently treated with heat. This is how:
- hepatic
- ;
- Chinese
- giant; lanceolated worms
- ;
- chance of the cat.
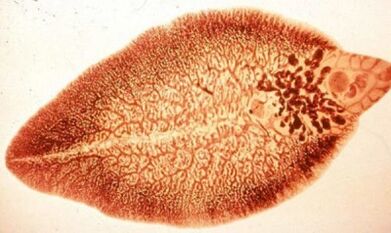
Sometimes a person is infected by direct contact: the larvae of the tropical parasites of schistosomias pierce the skin of people who swim in fresh water and then enter the bloodstream, in which they live and feed. of erythrocytes.
Most trematodes affect the liver, gallbladder and ducts of these organs, causing disease - trematodes. The living environment of a pulmonary worm is the muscles, the subcutaneous adipose tissue, the brain, but above all, the lungs. The disease caused by these helminths is called paragonimiasis. The small trematode metagonium lives in the small intestine, leading to metagonimose.
The worms are small in size - their flat, leaf-shaped body does not exceed 10 cm - however, the consequences of their permanence in the body of animals and humans are fatal. The long-term parasitism of these helminths can lead to the development of cancer, cirrhosis and gallstone disease.
Unlike trematodes, the body of tapeworms (cestodes) can reach tens of meters in length. The main route of infection with cestodes is through food. These helminths enter the human body with raw fish and meat. The main environment for the development of cestodes is the small intestine, in which adult worms live, while the larval forms live in the organs of the parenchyma (liver, lungs, spleen).
Of all tapeworms, the following are the most common:
- bullish tapeworm;
- echinococcus; wide tape
- ;
- pig tapeworm;
- alveococcus.
Round parasitic worms
Diseases caused by parasitic worms - nematodes - are first among all helminthiasis in terms of frequency of development. The habitat of most adult parasites is the intestines, but at certain stages of life they can migrate to the muscles, lungs, heart and pharynx. In the human population, the following nematodes are prevalent:
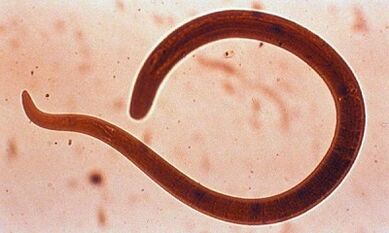
- pinworms;
- roundworm;
- toxocars;
- Trichinella; hookworms;
- Strongylides.
Roundworm eggs and larvae enter the human body through food and water. Nematodes themselves, such as hookworms and strongylids, invade the host's body. These helminths are found mainly in the tropics.
The ubiquitous nematodes are traits, roundworms and toxocaras. The former most often affects children, causing enterobiasis - the most common helminthiasis. Dogs carry Toxocara, although these nematodes can also infect humans. Roundworms live in humans and are not dangerous to most animals, with the exception of pigs.
Arthropod parasites
Cestodes, trematodes and parasitic nematodes are adapted to live in Organs internal organs of their hosts. In contrast, most parasitic arthropods live on the body's surface. Most of the time, a person becomes infected with lice and mites, the agents that cause demodicosis and scabies. These parasites are dangerous because they can carry pathogenic bacteria and rickettsia that cause Volyn's fever, typhus and recurrent fever.
Lice drink human blood and parasitic mites live on human skin. Scabies itches in the passages, the demodex lives in the hair follicles and in the ducts of the sebaceous glands. The vital activity of these parasites leads to allergies, accompanied by a rash, redness of the skin and itching.
The world we live in is developing rapidly, the standard of living is steadily increasing, and today it appears that many parasitic diseases are the fate of residents of third world countries. However, population migration leads to the spread of such pathologies beyond natural foci. In this regard, it is important to remember the basic rules of hygiene, the observance of which will help prevent infections.